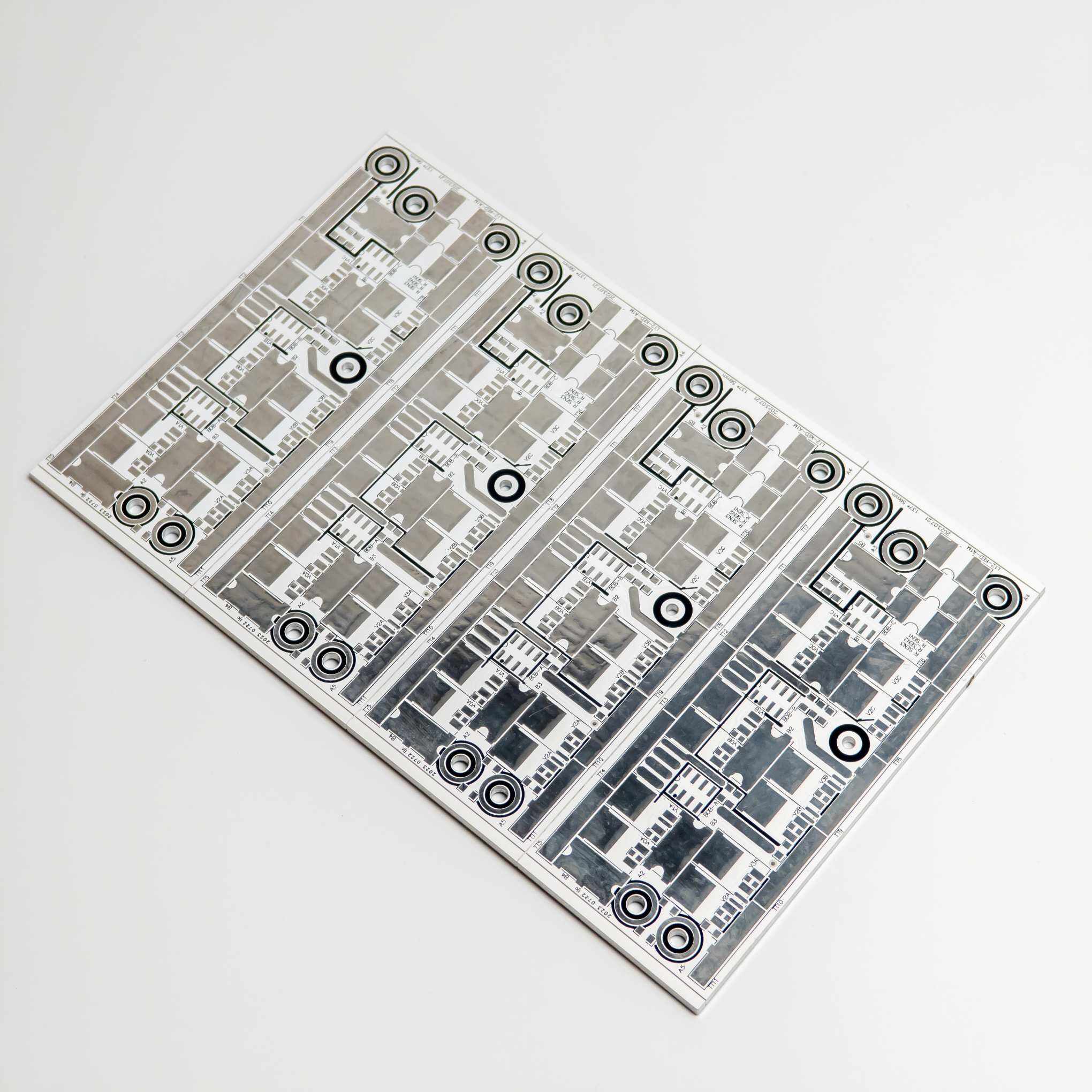
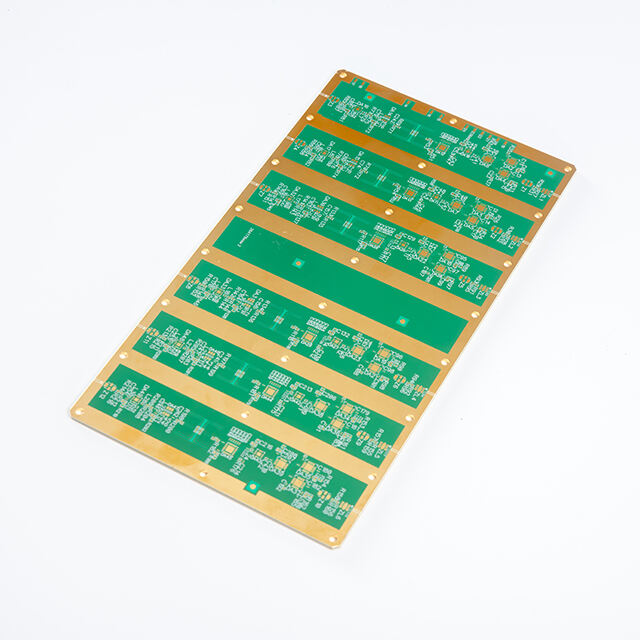
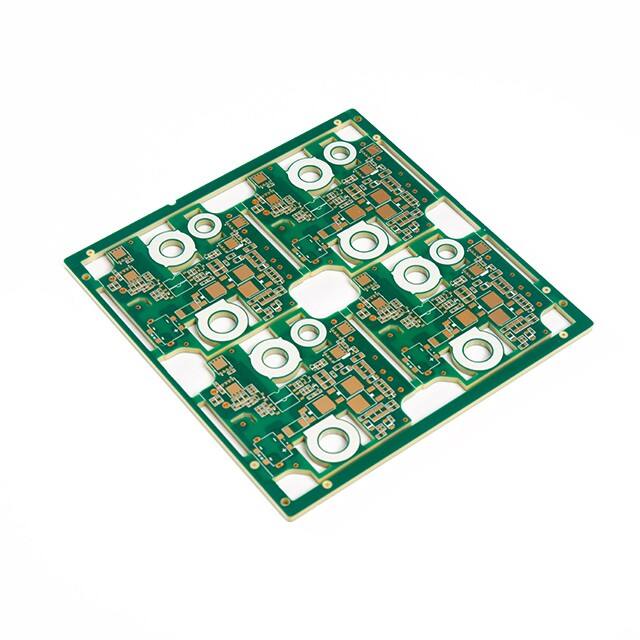
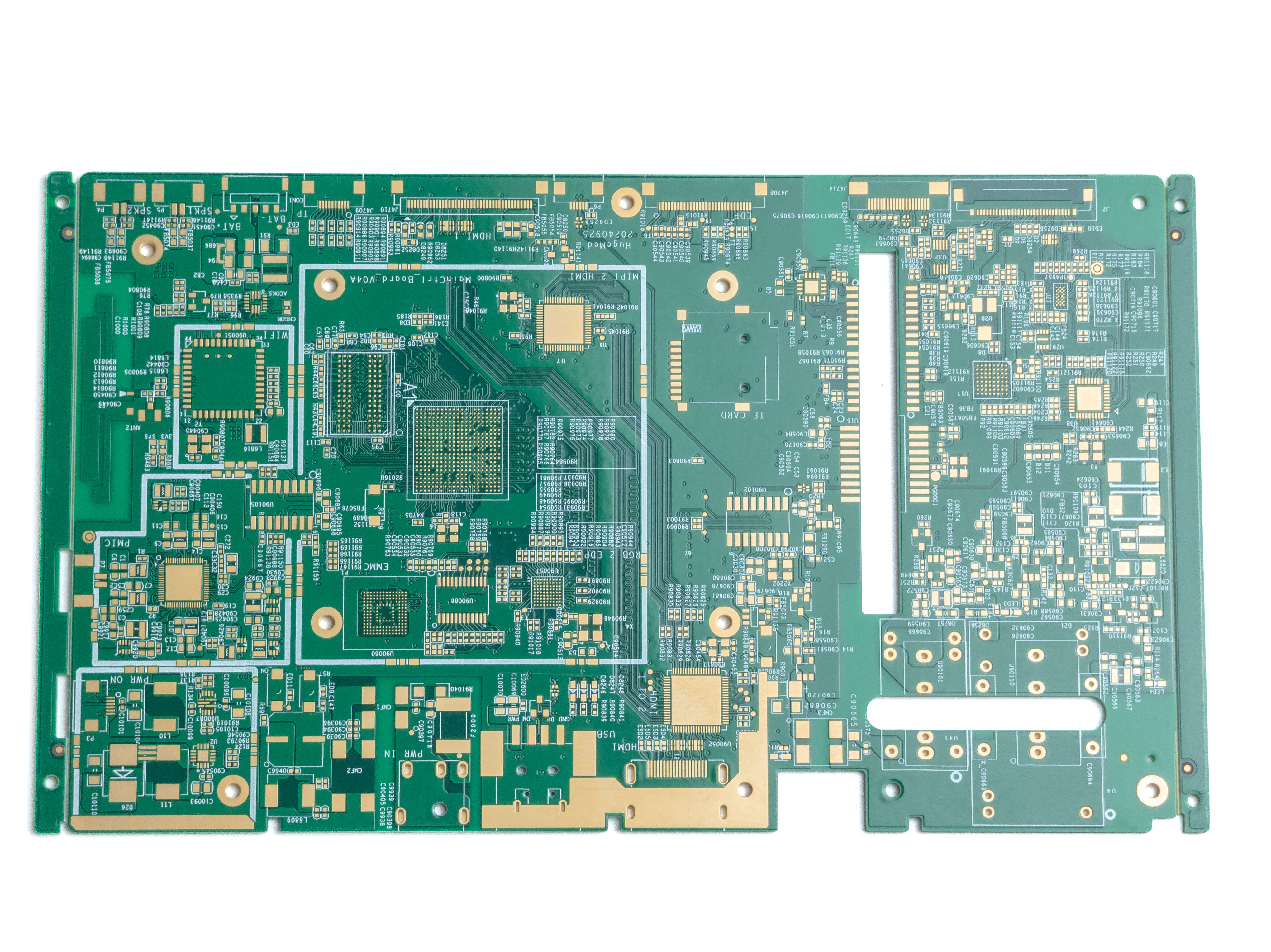
rigid pcb
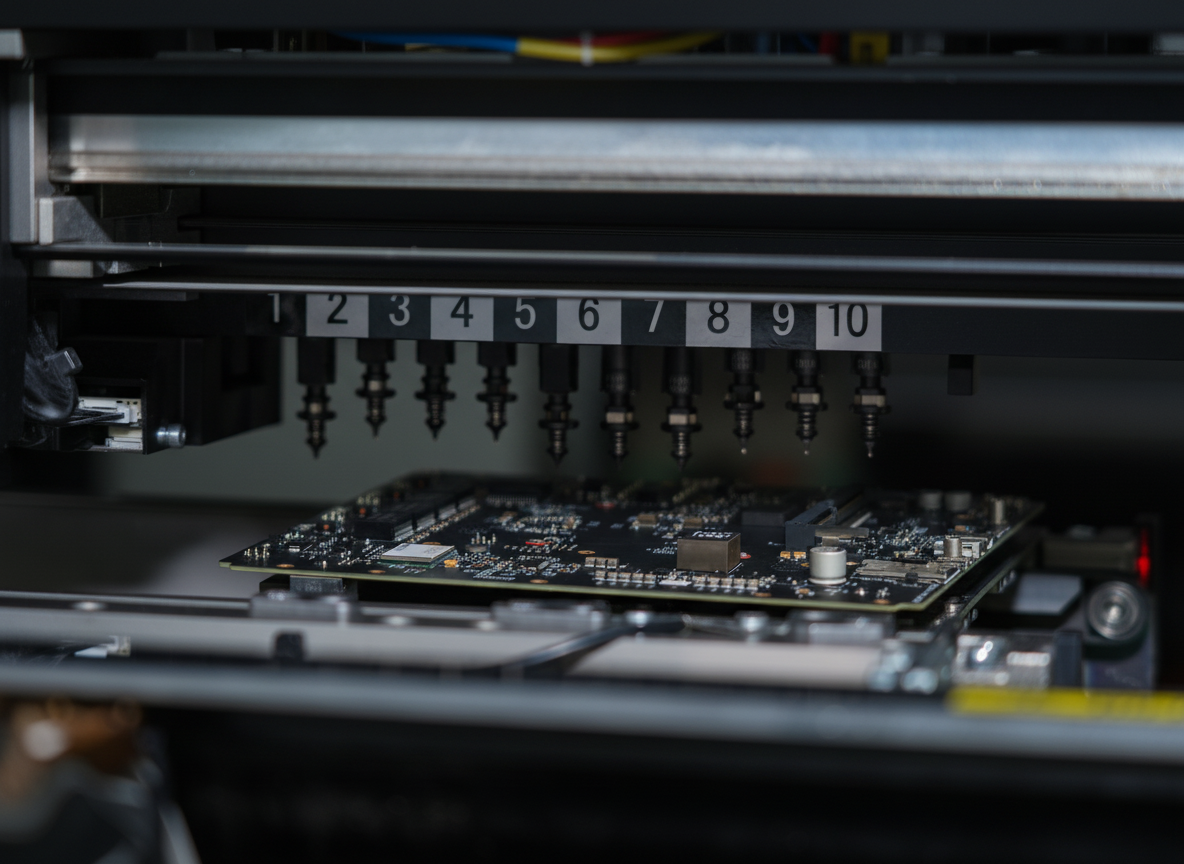
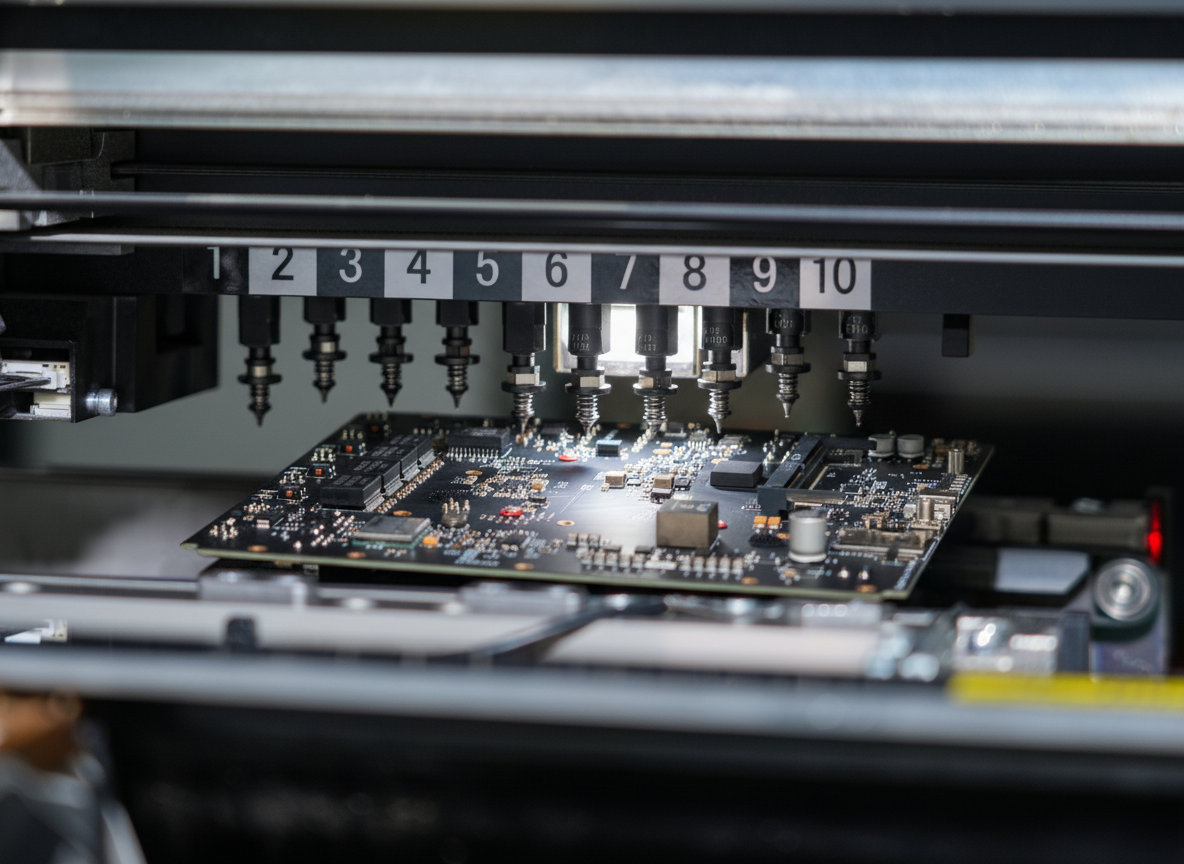
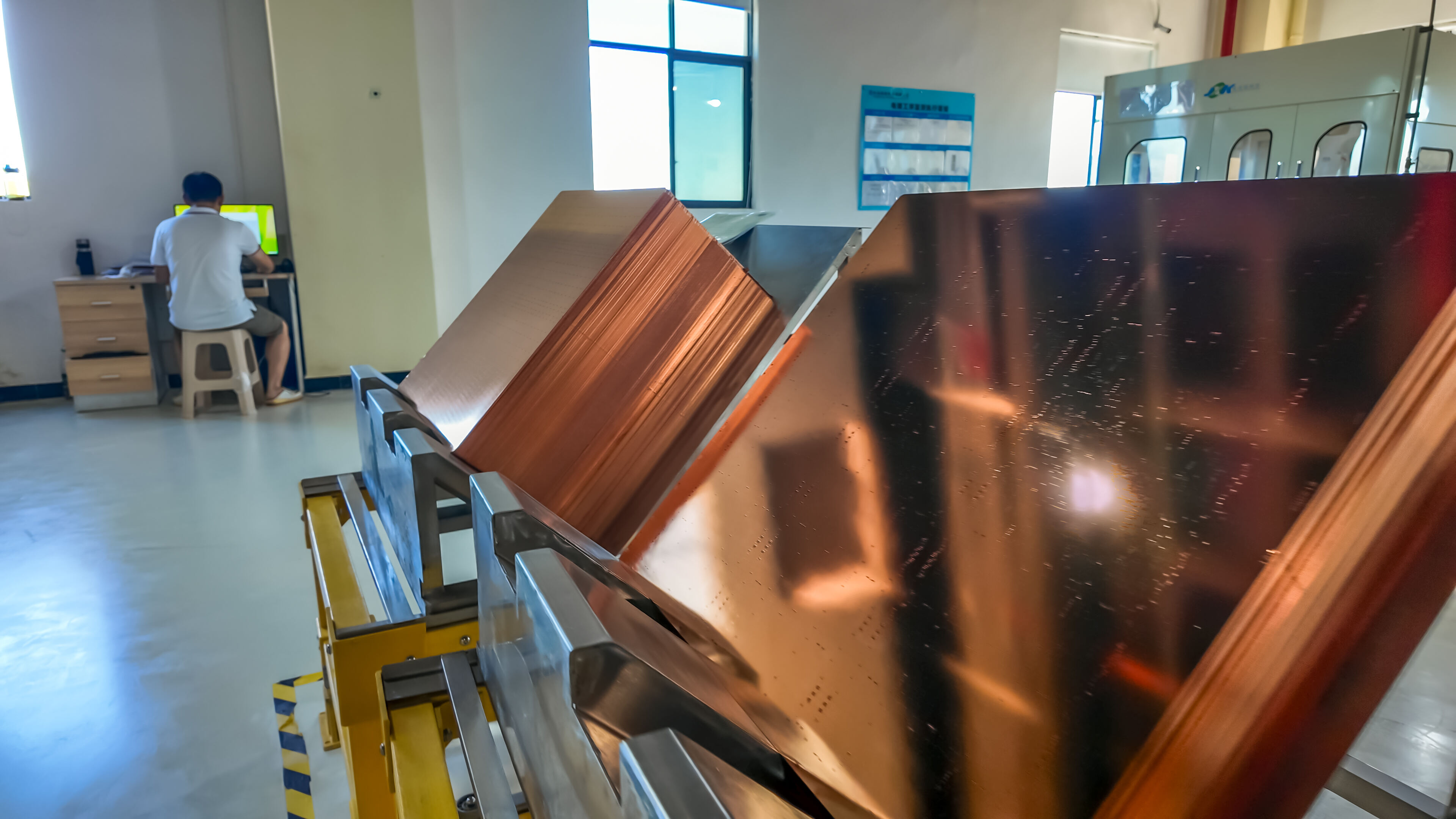
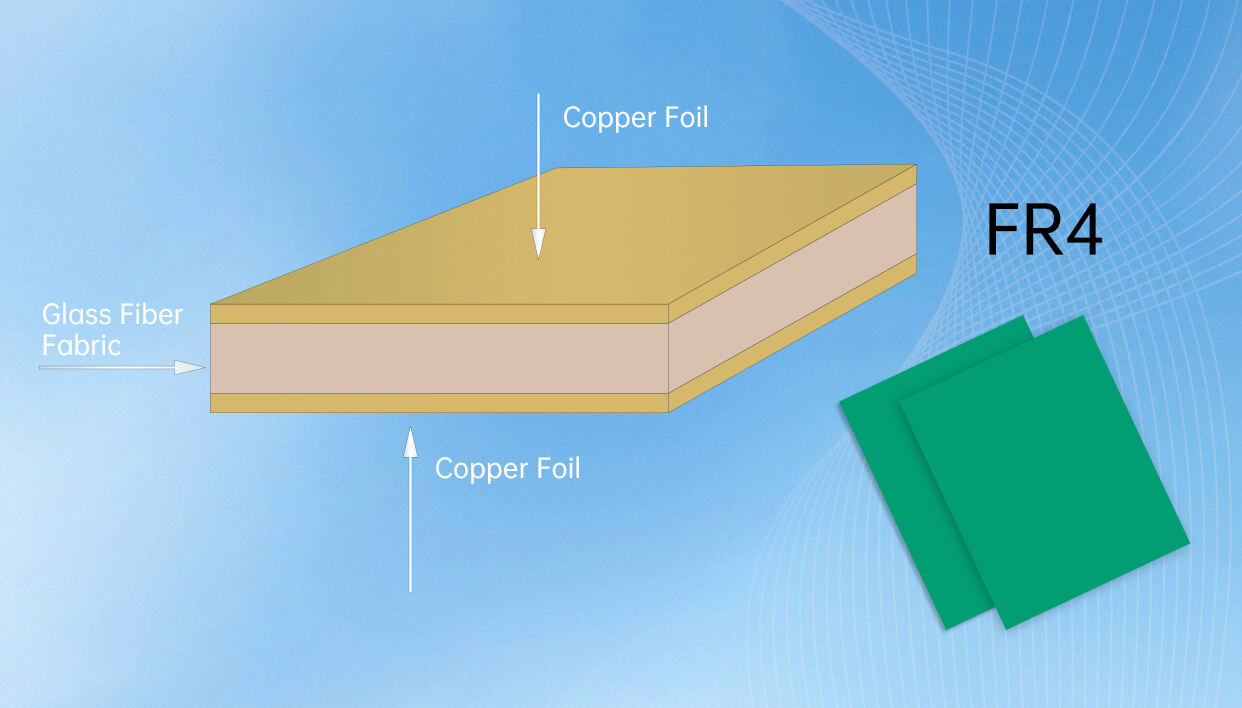
A rigid PCB (Printed Circuit Board) represents the foundation of modern electronic devices, serving as a reliable platform for mounting and interconnecting electronic components. These boards are fabricated from solid, non-flexible materials, typically consisting of multiple layers of copper-clad substrate material, most commonly FR4 glass-epoxy. The manufacturing process involves precise etching of copper traces to create conductive pathways, followed by the application of solder mask and silkscreen layers. Rigid PCBs excel in providing mechanical support and electrical connections for components such as integrated circuits, resistors, capacitors, and connectors. Their robust construction ensures excellent durability and reliability in various operating conditions, making them ideal for applications requiring long-term stability. These boards can be manufactured in single-layer, double-layer, or multi-layer configurations, offering different levels of circuit complexity and functionality. The design possibilities range from simple one-sided boards to sophisticated multilayer structures with high-density interconnections. Modern rigid PCBs often incorporate advanced features such as impedance control, buried vias, and thermal management solutions, enabling their use in high-frequency applications and complex electronic systems.