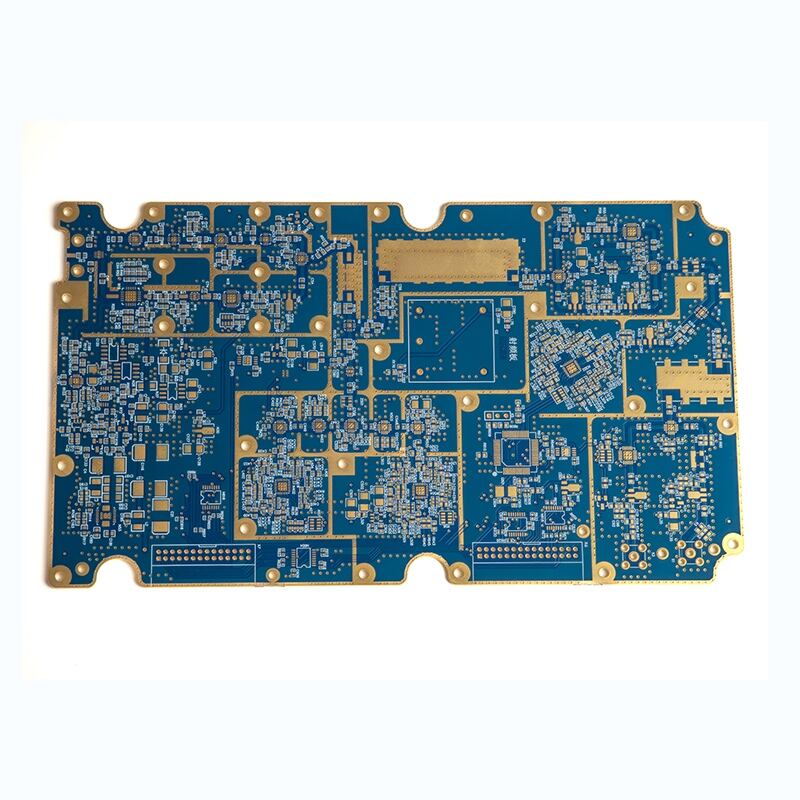
rigid circuit board
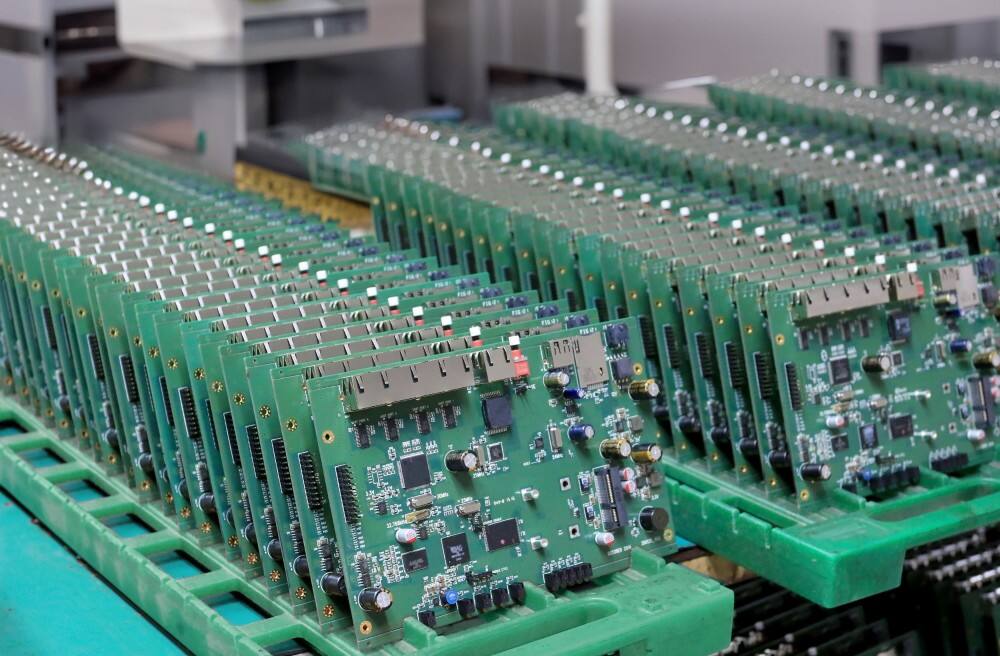
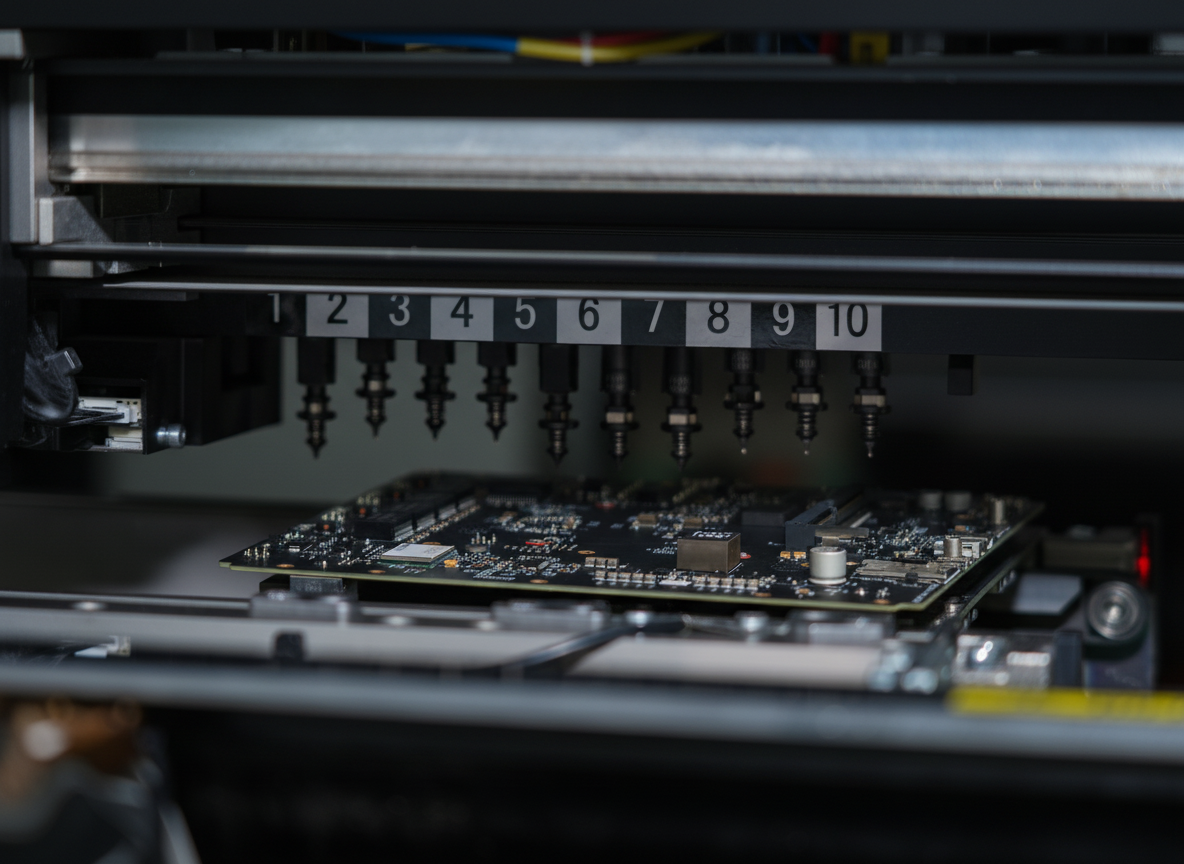
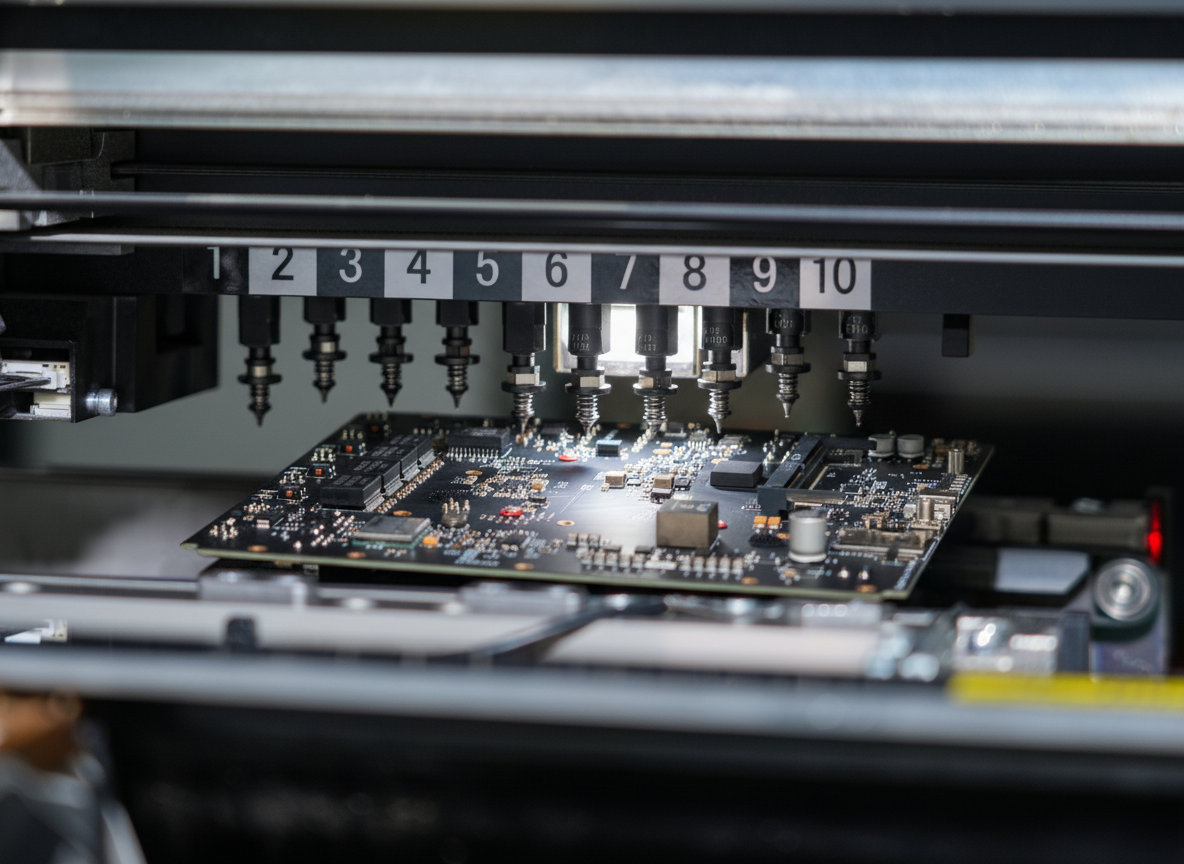
A rigid circuit board, also known as a rigid PCB, serves as the fundamental backbone of modern electronic devices, providing a solid and reliable platform for mounting and interconnecting electronic components. These boards are constructed from multiple layers of materials, primarily consisting of a non-conductive substrate, typically FR-4 glass-epoxy, and conductive copper layers. The rigid nature of these boards ensures excellent mechanical stability and protection for the electronic components they house. The manufacturing process involves precise layering of copper traces, which create the electrical pathways necessary for component communication. These boards can be single-sided, double-sided, or multi-layered, depending on the complexity of the circuit design and application requirements. The rigid structure allows for high-density component placement and reliable electrical connections, making them ideal for applications requiring robust performance and longevity. They are extensively used in consumer electronics, industrial equipment, automotive systems, and aerospace applications, where reliability and consistent performance are paramount. The boards undergo rigorous testing and quality control measures to ensure they meet specific industry standards and performance requirements.