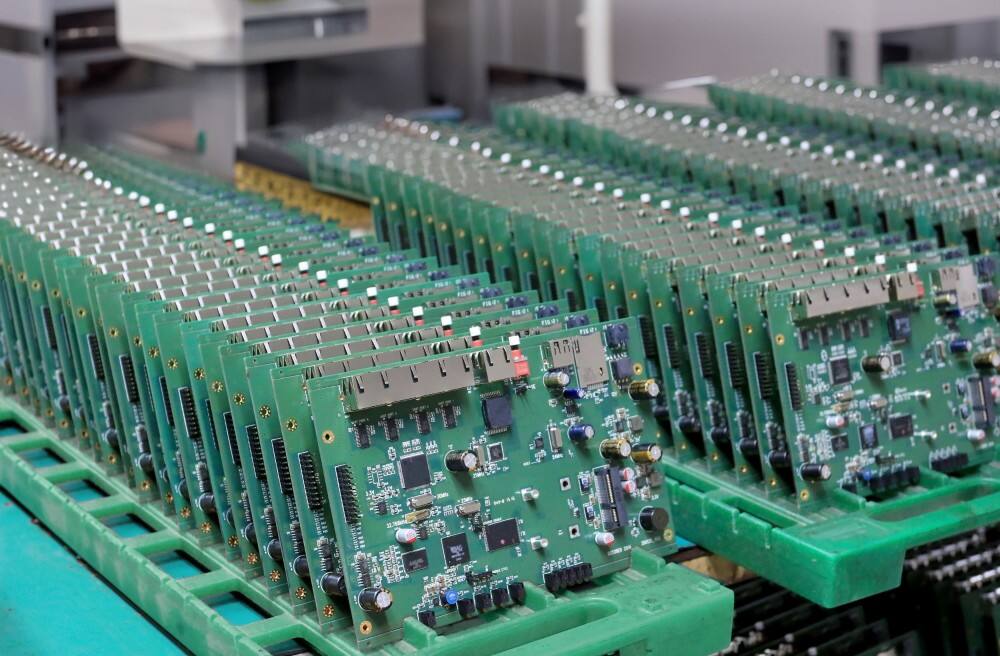
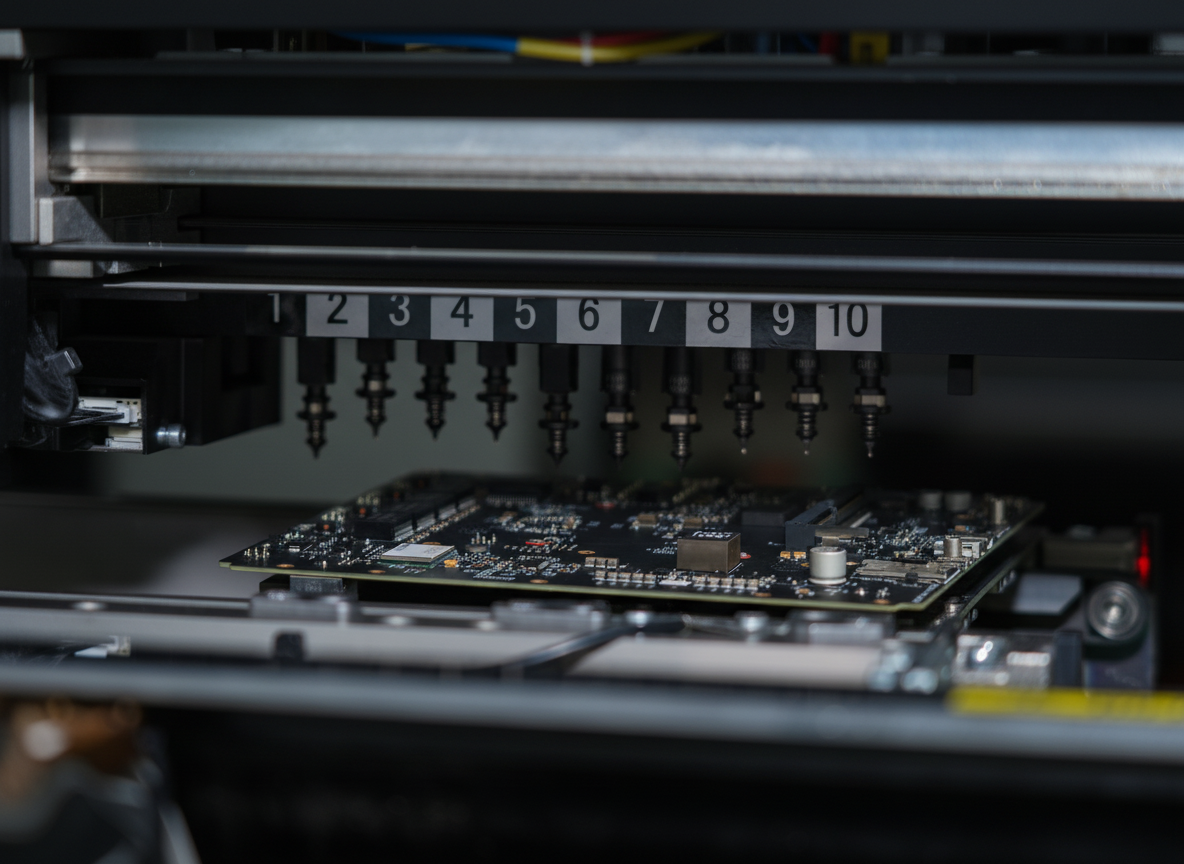
how to solder a pcb circuit board
Soldering a PCB circuit board is a fundamental skill in electronics that requires precision, proper technique, and the right tools. This process involves joining electronic components to a printed circuit board using molten solder, creating permanent electrical connections. The main steps include preparing the workspace with essential tools like a soldering iron, solder wire, flux, and safety equipment. Temperature control is crucial, typically ranging from 300-370°C for lead-free solder. The process begins with cleaning the PCB surface and components, applying flux to improve solder flow, then carefully heating both the component lead and pad simultaneously. The solder is applied to create a solid joint, characterized by a smooth, shiny appearance. Modern PCB soldering techniques incorporate lead-free solder compositions, meeting environmental regulations while maintaining reliable connections. This process is vital in electronics manufacturing, from consumer devices to industrial equipment, ensuring stable electrical connections and proper circuit functionality. Quality inspection post-soldering involves checking for proper solder coverage, absence of bridges between connections, and appropriate joint formation.