flexible printed circuit
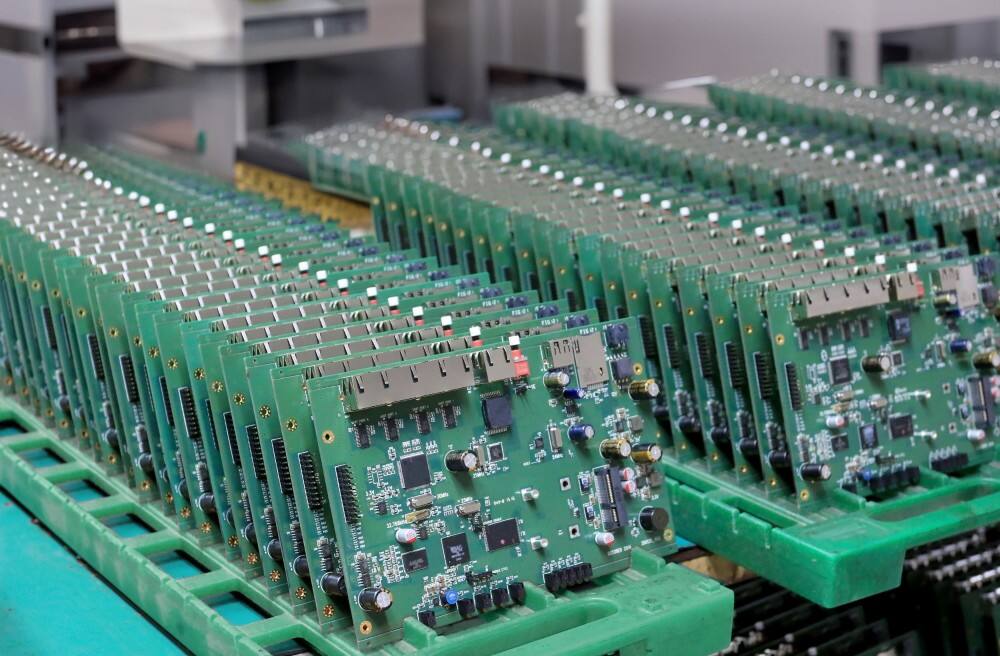
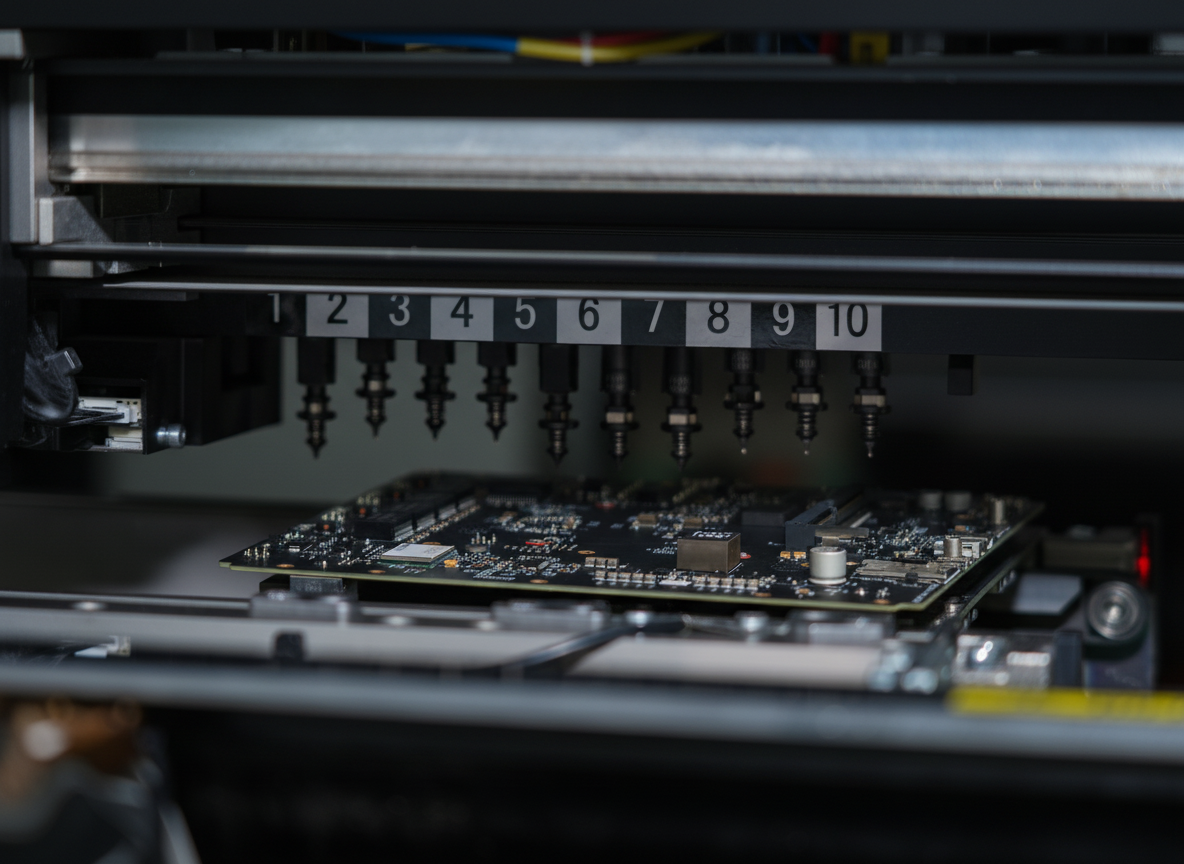
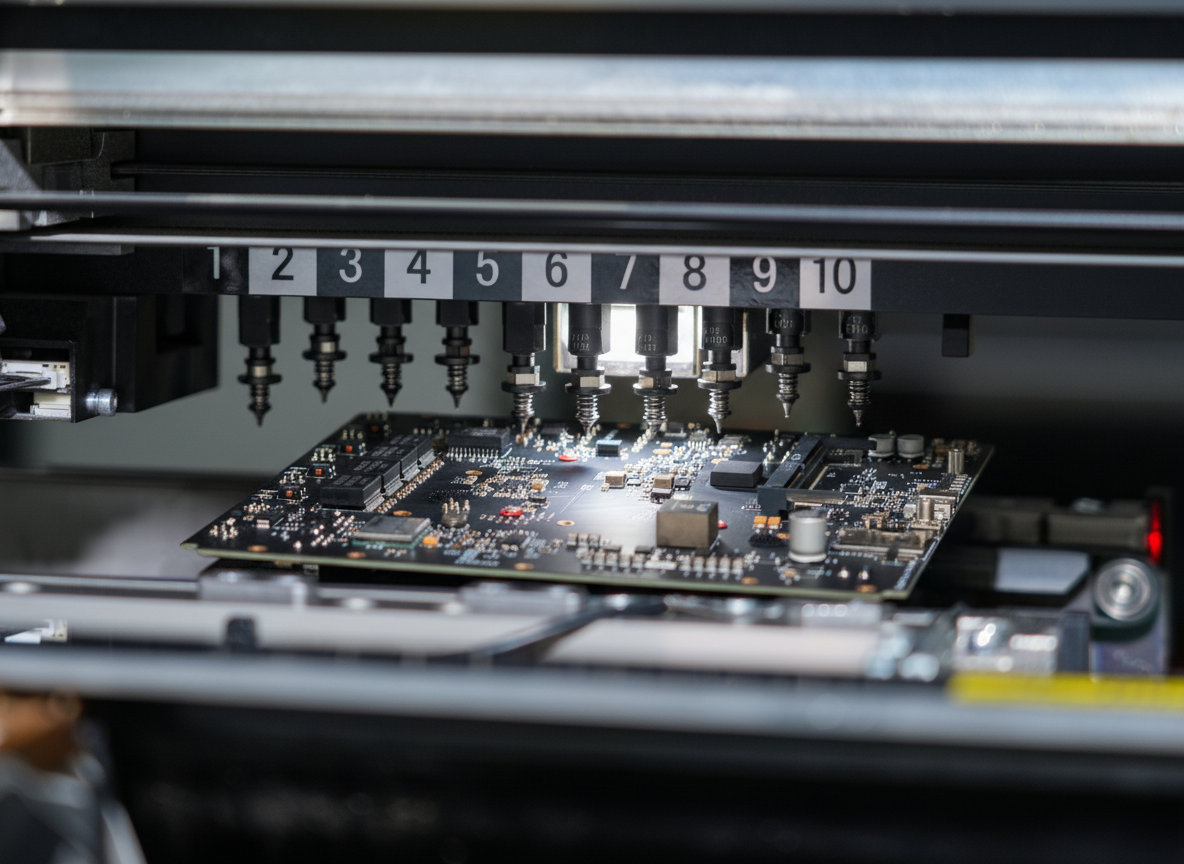
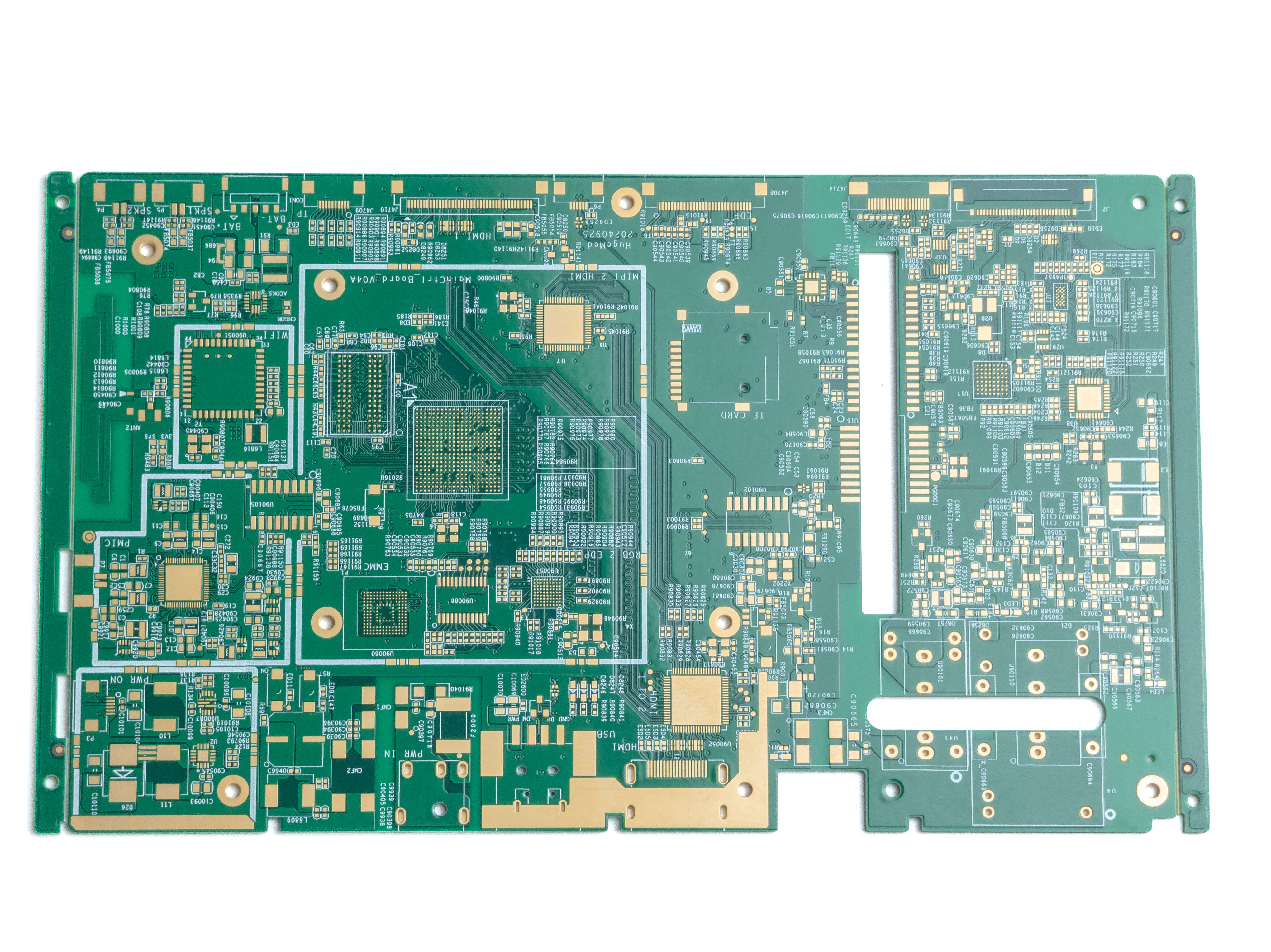
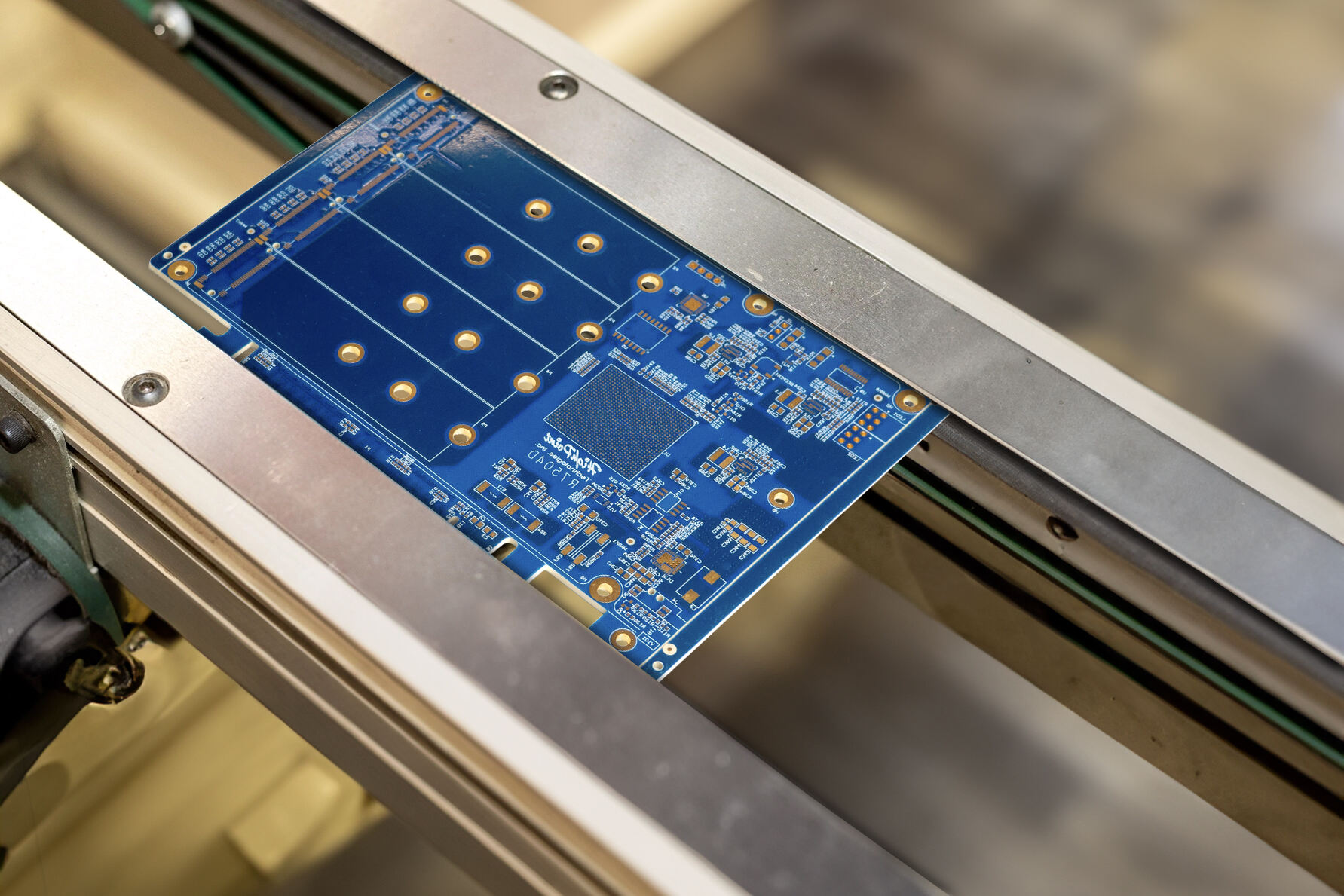
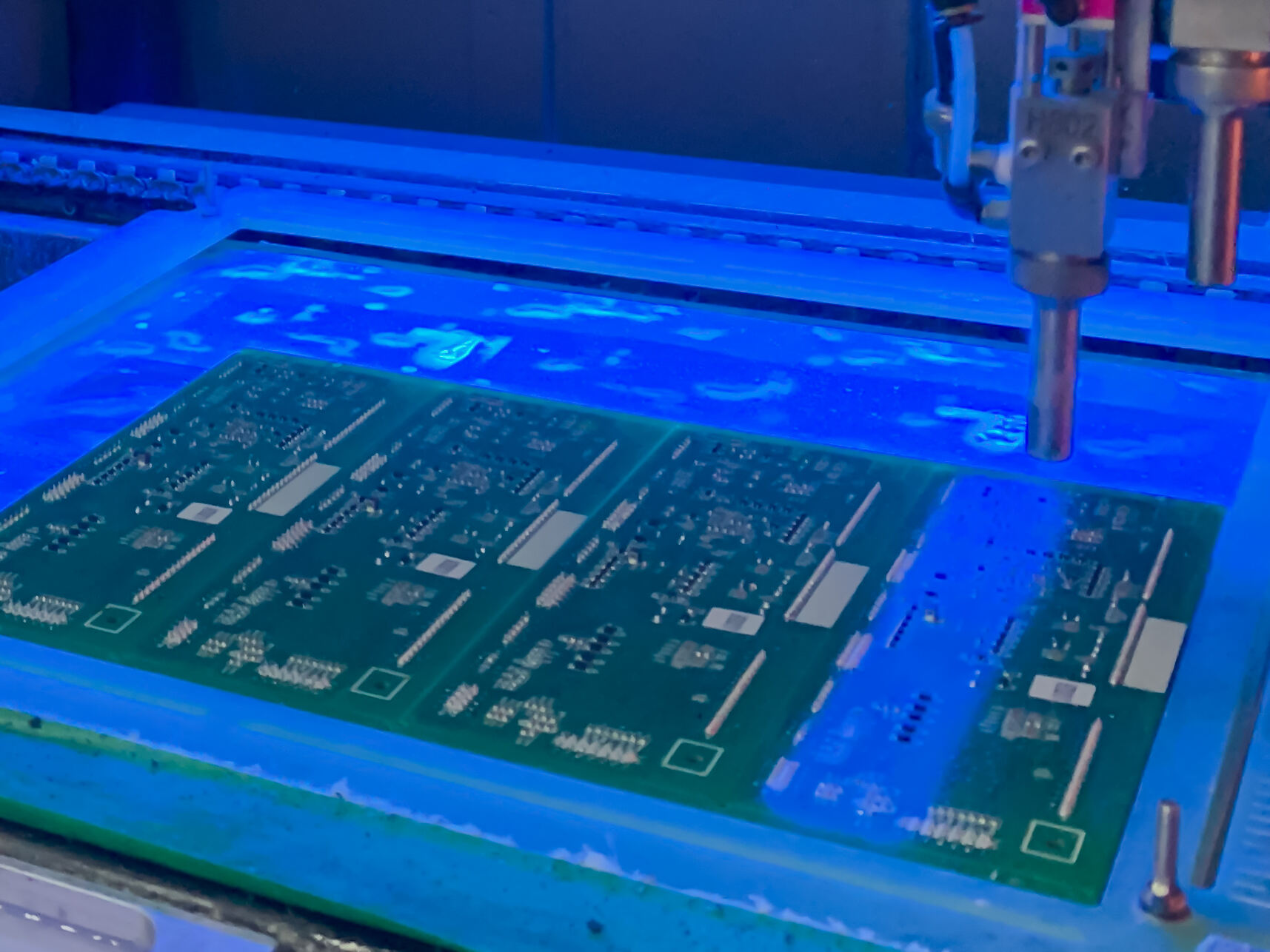
A flexible printed circuit (FPC) represents a groundbreaking technology in electronic manufacturing, combining the reliability of traditional printed circuit boards with the adaptability of flexible materials. These circuits are constructed using conductive patterns bonded to flexible substrate materials, typically polyimide or polyester films. The primary function of FPCs is to provide electrical connections while accommodating dynamic applications that require bending, folding, or fitting into irregular spaces. These circuits excel in applications where space constraints, weight requirements, and complex geometries pose challenges for rigid circuit boards. The technology features multiple layer capabilities, allowing for sophisticated circuit designs while maintaining minimal thickness. FPCs can integrate various electronic components, including surface mount devices, and can be designed with selective stiffening to support component mounting areas. They find extensive applications in modern electronics, from consumer devices like smartphones and laptops to advanced medical equipment and automotive systems. The manufacturing process involves precise layering of conductive materials, typically copper, onto the flexible substrate, followed by etching to create the desired circuit patterns. This technology has revolutionized electronic design by enabling three-dimensional electronic packaging solutions while maintaining reliable electrical performance.