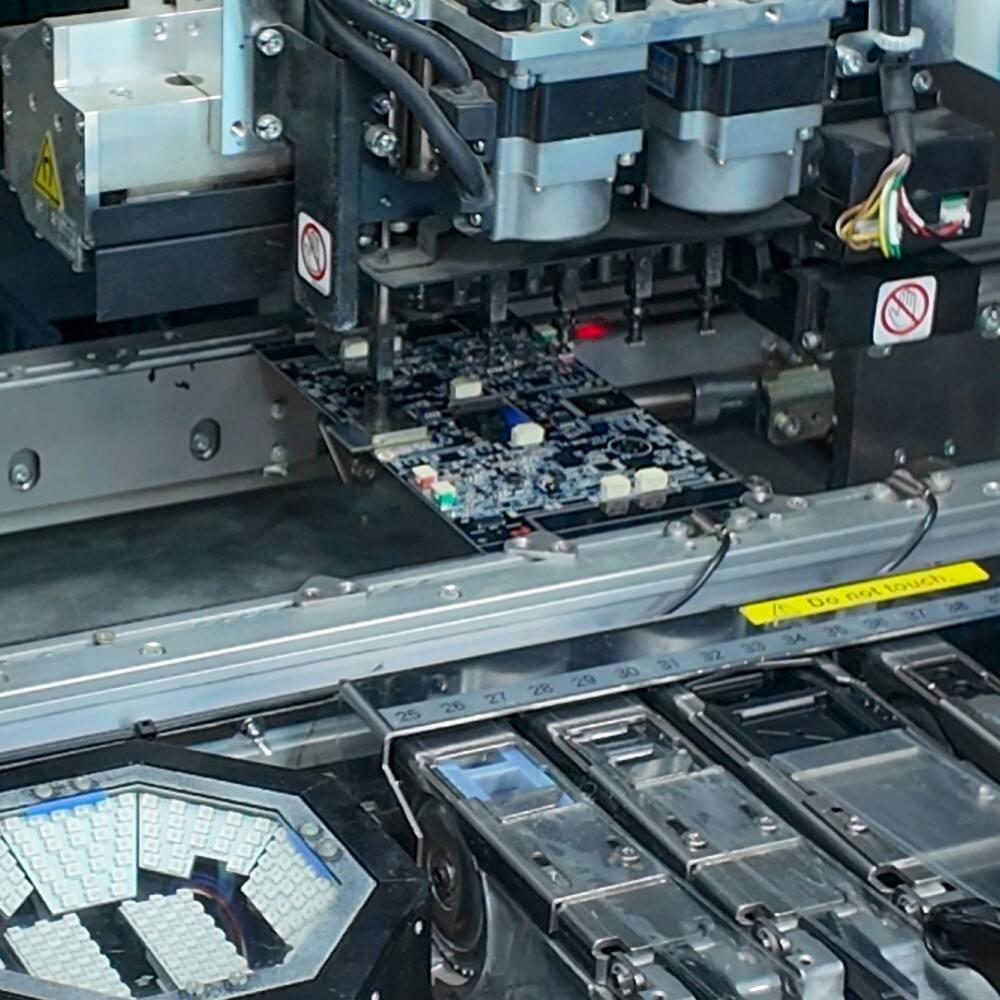
Surface Mount Technology has revolutionized the electronics manufacturing industry by enabling faster production cycles and significantly higher accuracy rates compared to traditional through-hole assembly methods. Modern manufacturers rely on SMT to achieve the precision and speed demanded by today's complex electronic devices, from smartphones to automotive control systems. The integration of automated placement equipment and advanced inspection systems has made SMT the preferred choice for high-volume production environments where consistency and reliability are paramount. This manufacturing approach has become essential for companies seeking to maintain competitive advantages while meeting stringent quality standards across various industrial applications.
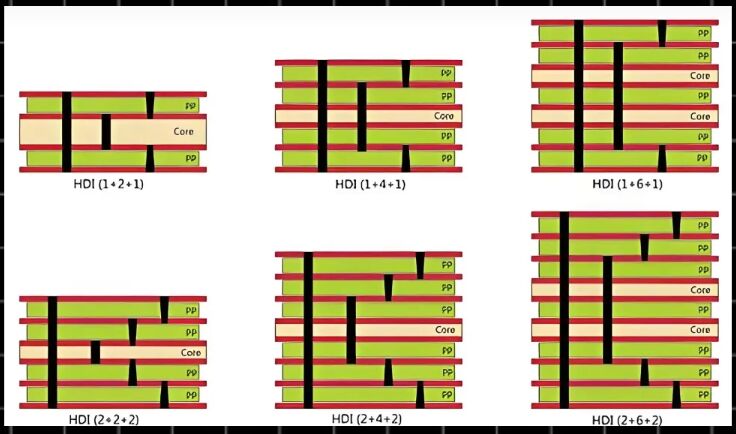
Understanding SMT Technology Fundamentals
Core Components and Equipment Systems
SMT manufacturing relies on sophisticated equipment systems that work together to achieve optimal placement accuracy and throughput rates. Pick and place machines form the backbone of SMT operations, utilizing high-speed vision systems and precision placement heads to position components with tolerances measured in micrometers. These automated systems can place thousands of components per hour while maintaining consistent accuracy across different component sizes and package types. The integration of conveyor systems, automatic optical inspection units, and reflow ovens creates a seamless production line that minimizes manual intervention and reduces potential error sources.
Stencil printing technology plays a crucial role in SMT accuracy by ensuring precise solder paste deposition across PCB pads. Modern stencil printers incorporate vision alignment systems and pressure monitoring capabilities that guarantee consistent paste volume and placement accuracy. The combination of laser-cut stencils and programmable squeegee systems enables manufacturers to achieve optimal solder joint formation while accommodating various component pitch requirements. This level of precision directly contributes to improved manufacturing yields and reduced rework requirements.
Process Control and Quality Assurance
Advanced process control systems monitor critical parameters throughout the SMT manufacturing cycle, enabling real-time adjustments that maintain optimal production conditions. Temperature profiling systems ensure reflow ovens maintain precise thermal cycles that promote proper solder joint formation while preventing component damage. Statistical process control methods track placement accuracy, solder paste volume, and inspection results to identify trends that could impact product quality. These monitoring systems provide manufacturers with the data needed to implement continuous improvement initiatives and maintain consistent production outcomes.
Quality assurance protocols in SMT environments typically include multiple inspection stages that verify component placement, solder joint integrity, and overall assembly quality. Automated optical inspection systems examine assemblies at various production stages, detecting defects that might affect functionality or reliability. X-ray inspection capabilities allow manufacturers to evaluate hidden solder joints, particularly important for components with connections beneath their packages. This comprehensive inspection approach ensures that defective assemblies are identified and corrected before they progress to subsequent manufacturing stages.
Speed Advantages in SMT Manufacturing
High-Speed Component Placement Capabilities
Modern SMT placement equipment achieves remarkable throughput rates through optimized machine architectures and intelligent placement algorithms. Multi-head placement systems can simultaneously handle different component types while maintaining precise positioning accuracy across the entire placement cycle. The integration of flexible feeders and component recognition systems enables rapid changeovers between different product configurations, minimizing setup time and maximizing production efficiency. These capabilities allow manufacturers to process mixed assemblies and varying production volumes without significant throughput penalties.
Placement optimization software analyzes component locations and sizes to determine the most efficient placement sequences, reducing machine cycle times and improving overall productivity. Advanced algorithms consider feeder locations, component orientation requirements, and placement head capabilities to minimize unnecessary movements during the assembly process. The result is significantly faster production cycles compared to manual assembly methods, with some systems achieving placement rates exceeding 100,000 components per hour. This speed advantage enables manufacturers to meet aggressive production schedules while maintaining consistent quality standards.
Parallel Processing and Automation Benefits
SMT production lines utilize parallel processing concepts that allow multiple assembly operations to occur simultaneously across different workstations. While one PCB undergoes component placement, others can simultaneously receive solder paste application, inspection, or reflow processing at adjacent stations. This parallel approach maximizes equipment utilization and minimizes overall cycle times compared to sequential assembly methods. The integration of buffer systems and intelligent material handling ensures smooth product flow between stations without bottlenecks or delays.
Automation extends beyond component placement to include material handling, quality inspection, and data collection functions that traditionally required manual intervention. Automated material supply systems maintain consistent component availability at placement machines, eliminating delays associated with manual feeder replenishment. Integrated data collection systems capture production metrics and quality information in real-time, enabling rapid response to process variations or quality issues. This comprehensive automation approach reduces labor requirements while improving consistency and traceability throughout the manufacturing process.
Precision and Accuracy Improvements
Vision System Integration and Alignment
Advanced vision systems incorporated into SMT equipment provide real-time feedback that ensures precise component placement and orientation accuracy. High-resolution cameras capture detailed images of components and PCB features, enabling automatic alignment corrections that compensate for variations in component positioning or PCB distortion. These vision systems can detect and correct placement errors within micrometers, significantly improving assembly reliability and reducing defect rates. The integration of machine learning algorithms enables vision systems to adapt to component variations and improve recognition accuracy over time.
Fiducial recognition capabilities allow SMT systems to automatically align with PCB reference points, ensuring consistent placement accuracy across different board designs and sizes. Global and local fiducial recognition systems provide multiple reference points that account for PCB warpage or distortion that might affect placement precision. The combination of board-level and component-level vision feedback creates a comprehensive alignment system that maintains accuracy throughout the entire assembly process. This precision capability is essential for fine-pitch components and high-density assemblies where placement tolerances are measured in fractions of component dimensions.
Consistent Solder Joint Formation
SMT processes achieve superior solder joint consistency through controlled paste deposition and precise reflow thermal profiles that ensure uniform metallurgical connections. Stencil printing systems deposit exact solder paste volumes at predetermined locations, eliminating the variability associated with manual soldering operations. The controlled atmosphere and temperature profiles used in reflow ovens promote optimal solder wetting and intermetallic compound formation that creates reliable electrical and mechanical connections. This consistency directly translates to improved product reliability and reduced field failure rates.
Temperature monitoring and control systems ensure that all solder joints experience identical thermal cycles, promoting uniform grain structure and mechanical properties across the entire assembly. Zone-controlled reflow ovens maintain precise temperature gradients that accommodate different component thermal requirements while preventing damage to sensitive devices. The elimination of manual soldering variables such as operator technique, iron temperature control, and flux application consistency results in dramatically improved solder joint quality and long-term reliability. This consistency advantage becomes increasingly important as component sizes decrease and circuit densities increase.
Industry Applications and Benefits
Consumer Electronics Manufacturing
Consumer electronics manufacturers leverage SMT technology to produce compact, feature-rich devices that meet demanding performance and cost requirements. The ability to place miniaturized components with high precision enables the development of smartphones, tablets, and wearable devices with advanced functionality in increasingly smaller form factors. SMT processes support the integration of complex multi-layer PCBs with hundreds or thousands of components while maintaining the manufacturing speeds required for high-volume consumer product production. The consistency and reliability achieved through SMT assembly directly impacts product quality and customer satisfaction in competitive consumer markets.
Cost advantages realized through SMT implementation include reduced material waste, lower labor requirements, and improved manufacturing yields that translate to competitive product pricing. Automated placement and inspection systems minimize rework requirements and scrap rates compared to manual assembly methods. The ability to process mixed component types and varying production volumes without significant setup penalties enables manufacturers to respond quickly to market demand fluctuations. These operational advantages are essential for success in fast-moving consumer electronics markets where time-to-market and cost competitiveness determine market share.
Industrial and Automotive Applications
Industrial control systems and automotive electronics benefit from SMT manufacturing through improved reliability and environmental resistance achieved through consistent assembly processes. The precision placement and controlled soldering environment create assemblies that withstand harsh operating conditions including temperature extremes, vibration, and chemical exposure. SMT processes enable the integration of advanced semiconductor devices and sensors that provide the intelligence required for modern industrial automation and vehicle control systems. The traceability and quality control capabilities inherent in SMT manufacturing support the documentation requirements common in industrial and automotive applications.
Automotive manufacturers particularly value the reliability improvements achievable through SMT assembly, as electronic system failures can impact vehicle safety and performance. The consistent solder joint formation and comprehensive inspection capabilities provided by SMT processes support the quality standards required for automotive electronics certification. Advanced driver assistance systems, engine management units, and infotainment systems rely on the density and reliability advantages provided by SMT assembly to deliver the functionality demanded by modern vehicles. The scalability of SMT manufacturing enables automotive suppliers to meet production volume requirements while maintaining the quality standards essential for automotive applications.
FAQ
What specific speed improvements can manufacturers expect when implementing SMT technology
Manufacturers typically experience assembly speed improvements of 300-500% when transitioning from manual or through-hole assembly methods to SMT processes. Modern placement machines can achieve rates of 50,000 to 150,000 components per hour depending on component mix and complexity, compared to manual placement rates of several hundred components per hour. The parallel processing capabilities of SMT lines further multiply these speed advantages by enabling simultaneous operations at multiple workstations. Additional time savings result from reduced setup times, automated material handling, and elimination of manual soldering operations that require individual attention to each connection point.
How does SMT technology improve placement accuracy compared to traditional methods
SMT systems achieve placement accuracies typically within ±25-50 micrometers compared to manual placement tolerances measured in hundreds of micrometers or more. Vision-guided placement systems continuously monitor and correct component positioning in real-time, compensating for variations in component dimensions, feeder positioning, or PCB distortion. The elimination of human factors such as fatigue, training variations, or environmental conditions ensures consistent placement accuracy throughout production runs. Advanced SMT systems incorporate machine learning capabilities that improve accuracy over time by analyzing placement results and optimizing correction algorithms.
What quality control advantages does SMT provide over conventional assembly methods
SMT manufacturing incorporates multiple automated inspection stages that provide comprehensive quality monitoring without slowing production cycles. Automated optical inspection systems can examine 100% of assemblies at multiple process stages, detecting defects that might be missed during manual inspection methods. Statistical process control systems track critical parameters and identify trends that could indicate process drift or equipment issues before they impact product quality. The documented process controls and traceability systems inherent in SMT manufacturing support quality certifications and provide detailed records for problem resolution or continuous improvement initiatives.
Can SMT technology accommodate both high-volume and prototype production requirements
Modern SMT equipment includes flexible configuration options that support efficient changeovers between different products without significant setup penalties. Programmable placement systems can quickly switch between component types and placement patterns through software changes rather than mechanical adjustments. Quick-change stencil systems and modular component feeders enable rapid transitions between different PCB designs and component requirements. Advanced SMT lines can efficiently process prototype quantities as small as single units or high-volume production runs exceeding millions of assemblies, making the technology suitable for diverse manufacturing scenarios from research and development through full-scale production.
Table of Contents
- Understanding SMT Technology Fundamentals
- Speed Advantages in SMT Manufacturing
- Precision and Accuracy Improvements
- Industry Applications and Benefits
-
FAQ
- What specific speed improvements can manufacturers expect when implementing SMT technology
- How does SMT technology improve placement accuracy compared to traditional methods
- What quality control advantages does SMT provide over conventional assembly methods
- Can SMT technology accommodate both high-volume and prototype production requirements