The Evolution of Modern PCB Manufacturing Excellence
In today's increasingly connected world, PCB manufacturing stands at the heart of electronic innovation. From smartphones to advanced medical devices, printed circuit boards serve as the foundation for virtually every electronic device we rely on. The intricate process of PCB manufacturing has evolved significantly over the decades, incorporating cutting-edge technologies and rigorous quality control measures to meet the demanding standards of modern electronics.
The journey from design to finished product involves multiple sophisticated steps, each requiring precise attention to detail and adherence to strict quality protocols. As electronic devices become more complex and miniaturized, the importance of maintaining exceptional standards in PCB manufacturing cannot be overstated. Industry leaders continuously refine their processes to achieve unprecedented levels of precision while maintaining consistency across high-volume production runs.
Core Components of Quality PCB Production
Material Selection and Preparation
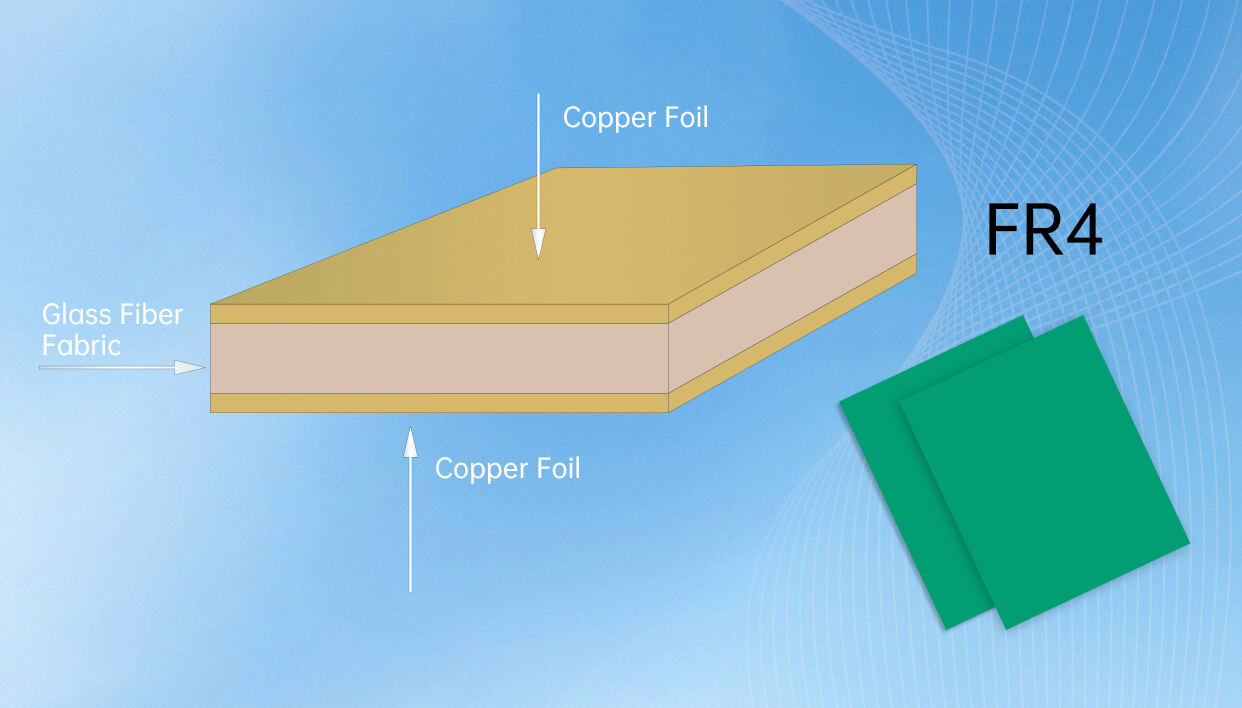
The foundation of superior PCB manufacturing begins with the careful selection of base materials. High-quality substrate materials, typically FR-4 glass-reinforced epoxy laminate, must meet specific thermal, mechanical, and electrical requirements. Manufacturers carefully evaluate factors such as dielectric constant, glass transition temperature, and thermal expansion coefficients to ensure optimal performance in the final product.
Before production begins, these materials undergo thorough testing and preparation. The copper foil used for conductors must meet strict purity standards, while the prepreg materials that bond the layers together require precise handling and storage conditions. Advanced PCB manufacturing facilities maintain controlled environments to prevent contamination and ensure consistent material properties throughout the production process.
Advanced Manufacturing Technologies
Modern PCB manufacturing relies heavily on automated systems and precision equipment. Computer-controlled drilling machines create holes with accuracy down to microns, while sophisticated imaging systems ensure precise alignment of circuit patterns. Laser drilling technology enables the creation of incredibly small vias, essential for high-density interconnect (HDI) boards used in advanced electronics.
Surface mount technology (SMT) has revolutionized PCB manufacturing by allowing for higher component density and improved reliability. Automated optical inspection (AOI) systems scan boards at multiple stages of production, detecting even the smallest defects that might compromise performance. These technologies work in concert to maintain consistency and precision throughout the manufacturing process.

Quality Control Measures in PCB Production
Inspection and Testing Protocols
Rigorous inspection protocols form the backbone of quality assurance in PCB manufacturing. Every board undergoes multiple rounds of testing, starting with basic visual inspections and progressing to sophisticated electronic testing. X-ray inspection systems reveal hidden defects in internal layers, while flying probe testers verify electrical connectivity and component functionality.
Environmental stress screening (ESS) subjects boards to controlled temperature and humidity variations, ensuring they can withstand real-world operating conditions. Manufacturers also employ impedance testing, particularly crucial for high-frequency applications where signal integrity is paramount. These comprehensive testing procedures help identify and eliminate potential issues before boards leave the facility.
Documentation and Traceability
Modern PCB manufacturing facilities maintain detailed documentation of every production batch. Each board receives unique identifiers that enable complete traceability throughout its lifecycle. This system allows manufacturers to track materials, process parameters, and test results, facilitating quick identification and resolution of any issues that may arise.
Quality management systems (QMS) integrate with production workflows, ensuring consistent adherence to established procedures and standards. Regular audits and reviews help identify opportunities for process improvement while maintaining compliance with industry certifications such as ISO 9001 and IPC standards.
Environmental Considerations and Sustainability
Green Manufacturing Practices
Leading PCB manufacturing facilities increasingly implement environmentally conscious practices. Water recycling systems minimize waste, while advanced filtration technology reduces harmful emissions. The adoption of lead-free soldering processes and RoHS-compliant materials demonstrates the industry's commitment to environmental responsibility.
Waste reduction strategies extend beyond materials to include energy efficiency measures and optimal resource utilization. Many facilities now use renewable energy sources and implement smart factory systems to minimize their carbon footprint while maintaining high-quality standards in production.
Future-Ready Manufacturing
The future of PCB manufacturing lies in smart factory integration and Industry 4.0 principles. Advanced data analytics help optimize production parameters in real-time, while artificial intelligence systems predict and prevent potential quality issues. These innovations ensure sustainable manufacturing practices while meeting increasingly stringent quality requirements.
Manufacturers are also investing in research and development to explore new materials and processes that offer improved performance with reduced environmental impact. This forward-thinking approach helps ensure the industry remains both competitive and environmentally responsible.
Frequently Asked Questions
What factors most significantly impact PCB manufacturing quality?
The most crucial factors affecting PCB manufacturing quality include material selection, process control parameters, environmental conditions during production, and the sophistication of testing and inspection systems. Additionally, operator training and quality management systems play vital roles in maintaining consistent standards.
How do manufacturers ensure consistency across high-volume production runs?
Consistency in high-volume PCB manufacturing is achieved through automated production systems, real-time monitoring of process parameters, regular calibration of equipment, and comprehensive quality control protocols. Statistical process control methods help identify and correct variations before they affect product quality.
What advancements are shaping the future of PCB manufacturing?
The future of PCB manufacturing is being shaped by developments in artificial intelligence, machine learning for quality control, advanced materials science, and Industry 4.0 integration. These technologies enable greater precision, improved efficiency, and enhanced quality assurance while supporting sustainable manufacturing practices.
How do environmental considerations affect PCB manufacturing processes?
Environmental considerations influence material selection, waste management procedures, energy usage, and chemical handling in PCB manufacturing. Modern facilities implement green technologies and sustainable practices while maintaining strict quality standards, demonstrating that environmental responsibility and manufacturing excellence can coexist.